In-Depth Analysis of High-Power LED Chips: Parameters, Performance, and Internal Structure

Even today, many experienced drivers still firmly believe that halogen headlights are the best headlights. This mindset is similar to how some people still think the old iPhone 4 was the best phone ever made.
Part of that comes from design and era memories, part from nostalgia, and part from the fact that halogen headlights were, in many ways, actually not bad at all. To understand why, we need to look at history, driving experience, and technology.
1. High-Power LED Chips: An Overview
High-power LED chips have become the cornerstone of modern lighting solutions, offering significant advantages in energy efficiency, lifespan, and environmental impact compared to traditional lighting technologies like halogen.
2. What Are "High-Power LED Chips" and Their Advantages
2.1 Definition and Classification
High-power LED chips typically refer to LED light sources with a rated current exceeding 100mA and a power of 1W or higher. Commonly available on the market are 1W, 3W, and 5W single LEDs, as well as COB (Chip-on-Board) light sources, with power often reaching tens or even hundreds of watts. Depending on the power and packaging, they can be used in various scenarios, from household spotlights to large industrial and mining lamps and streetlights.
2.2 Working Principle
The light-emitting process of an LED involves current passing through a semiconductor chip, where electrons and holes recombine and release energy in the form of photons. This process is highly efficient, converting electrical energy into light energy at a much higher rate than traditional incandescent or fluorescent lamps, while also generating less heat, resulting in a longer lifespan.
2.3 Advantages of High-Power LED Chips
- Energy Efficiency: More electrical energy is converted into light energy rather than heat energy, resulting in significantly lower energy consumption than incandescent lamps.
- Long Lifespan: LED chips have a lifespan far exceeding that of traditional light bulbs, capable of emitting light continuously for thousands to tens of thousands of hours.
- Environmentally Friendly and Safe: Contains no harmful substances such as mercury, generates little heat, and reduces safety hazards.
- Flexible Light Color: Through different chip, phosphor, and packaging designs, various color temperatures and light colors can be achieved to adapt to different application scenarios.
3. Understanding the "Specification Sheet": How to Read the "ID Card" of an LED Chip
3.1 Key Parameters
- Power (W) and Luminous Flux (lm): Power reflects energy consumption, while luminous flux reflects brightness. High-quality LEDs emit high brightness even at low power.
- Color Temperature (K) and Color Rendering Index (CRI): Color temperature determines the "hue" of light, and CRI measures the accuracy of color reproduction.
- Emitting Angle and Luminous Efficacy: The emitting angle affects light distribution, while luminous efficacy (lm/W) is an important indicator of energy-saving performance.
4. Internal Structure and Key Materials of LED Chips
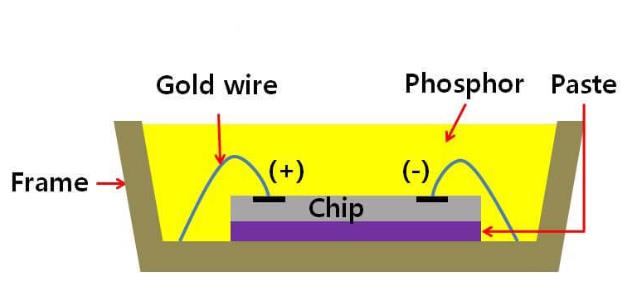
The internal structure of high-power LED chips consists of multiple precision components that directly affect performance and lifespan:
- LED Chip: The core light-emitting element that determines brightness, efficiency, and lifespan.
- Gold Wire + Solder Joint + Frame: Gold wires serve as conductive and heat-conducting paths. Solder joints should be full and smooth. Frames are typically made of copper or aluminum for good heat conduction.
- Phosphor: White LEDs use a blue chip and yellow phosphor. The phosphor formulation and coating process affect color consistency and color rendering.
- Encapsulation (Lens/Resin): Encapsulation protects the internal structure and influences light emission efficiency, beam angle, and heat dissipation.
- Substrate/Heat Dissipation: The substrate is responsible for dissipating heat to prevent the chip from overheating, ensuring longevity and performance.
5. Why Do LEDs Dim or Have Shortened Lifespans?
LED chips can experience dimming or shortened lifespans due to the following factors:
- Chip Aging: High temperatures cause LED chip efficiency to decrease over time.
- Phosphor Aging: Phosphor efficiency decreases under prolonged exposure to high temperatures, leading to reduced brightness.
- Encapsulation Material Aging: Encapsulation materials may degrade due to heat, reducing light transmittance.
- Poor Heat Dissipation: Inadequate heat dissipation design leads to heat accumulation, which shortens the lifespan.
6. Wiring Methods: Series vs. Parallel – Advantages and Disadvantages Comparison
6.1 Series Connection
- Multiple LED chips connected end-to-end. The total voltage is the sum of individual chips.
- Advantages: Requires only one constant current power supply.
- Disadvantages: If one chip fails, the entire series connection will stop working.
6.2 Parallel Connection
- All positive terminals are connected together, and all negative terminals are also connected together.
- Advantages: Failure of one chip does not affect others.
- Disadvantages: Requires high chip consistency, as slight differences can lead to uneven current distribution and reduced lifespan.
7. How to Evaluate LED Chip Quality: From Appearance to Performance Testing
7.1 Appearance Inspection
- Chip Size: Larger chips generally indicate better heat dissipation.
- Gold Wire: Gold wires should be thick and clear without breaks or impurities.
- Soldering: Solder joints should be smooth and full, with no cold or poor soldering.
- Encapsulating Adhesive/Lens: The encapsulant or lens should be clear and transparent, free of bubbles and impurities.
7.2 Performance Testing
- Light Spot: Check for uniformity and clarity of the light spot.
- Color Consistency: Check for significant color differences between multiple LEDs.
- Flicker Detection: Use a mobile phone camera to check for flickering, which indicates power supply or LED issues.
8. Choosing the Right LED: Understanding Key Details to Avoid Quality Pitfalls
High-power LED chips may seem complex, but focusing on factors like luminous efficacy (lm/W), color temperature, CRI, heat dissipation, and packaging design will help you select a truly high-quality, durable LED chip.
